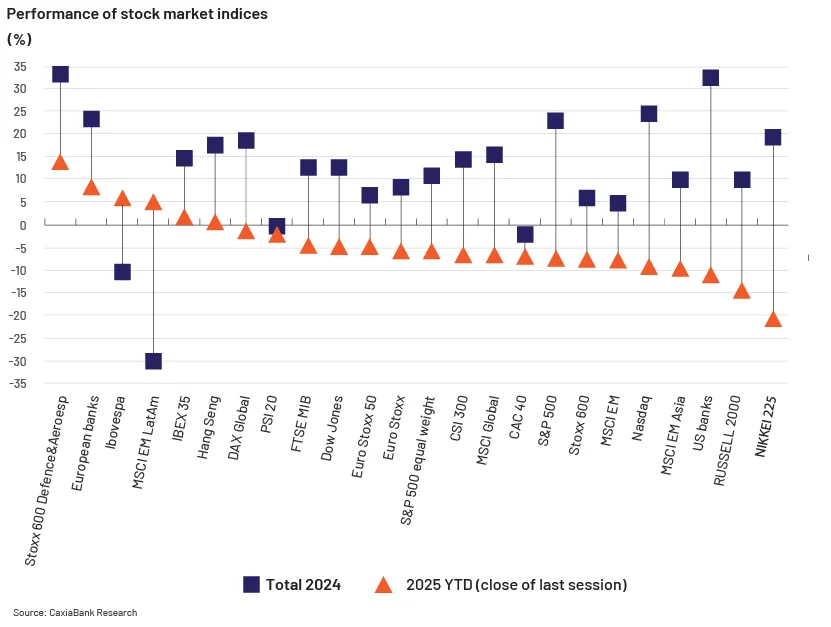
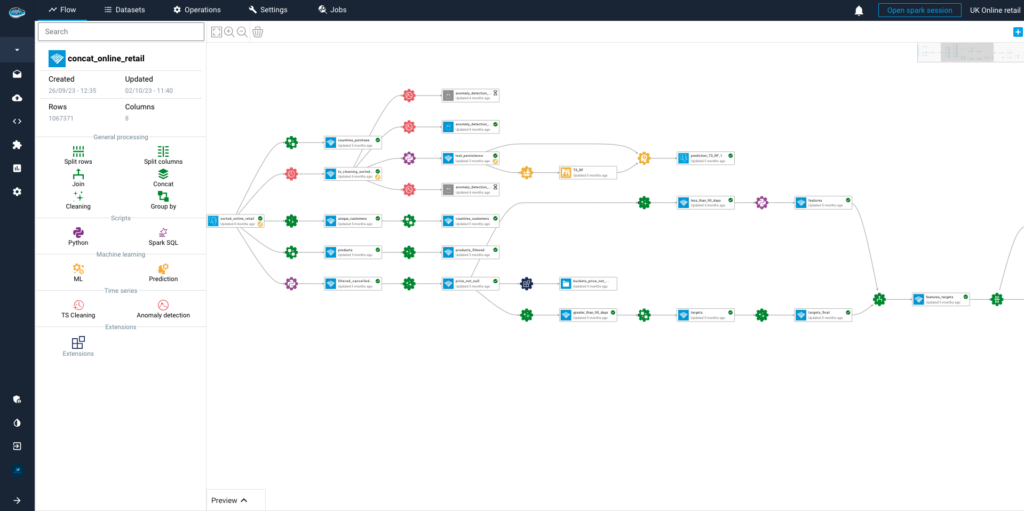
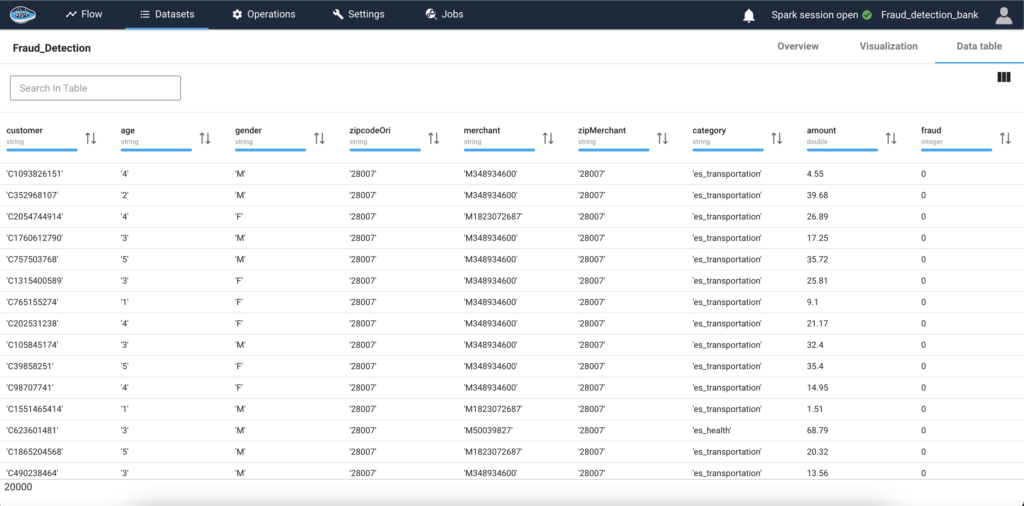
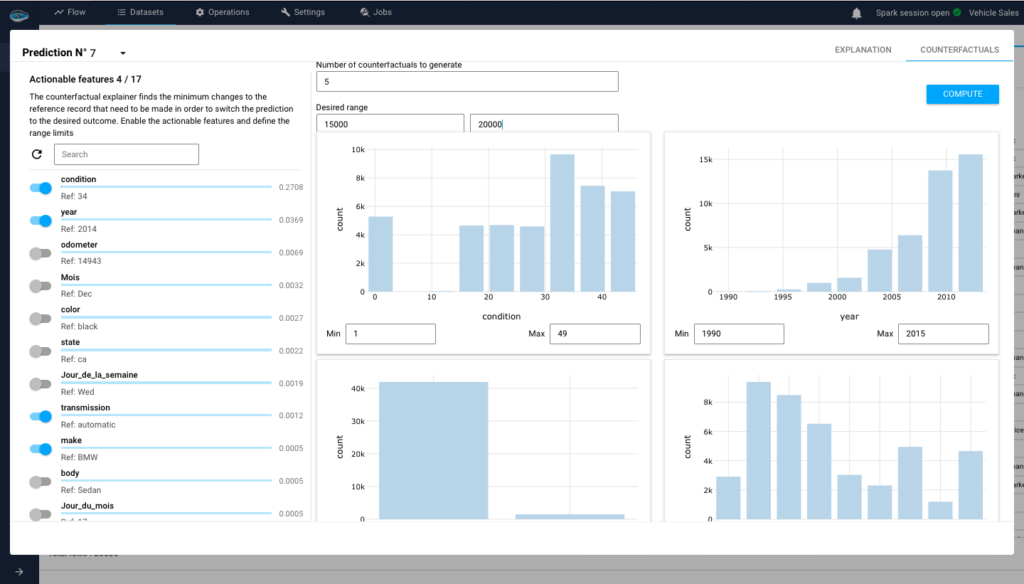
Why Should You Consolidate Your AI Tools for Faster Scaling?...
Read MoreIn this article, we’ll explore the ripple effects of tariff volatility on global supply chains and more importantly, how companies can respond with agility by leveraging artificial intelligence.