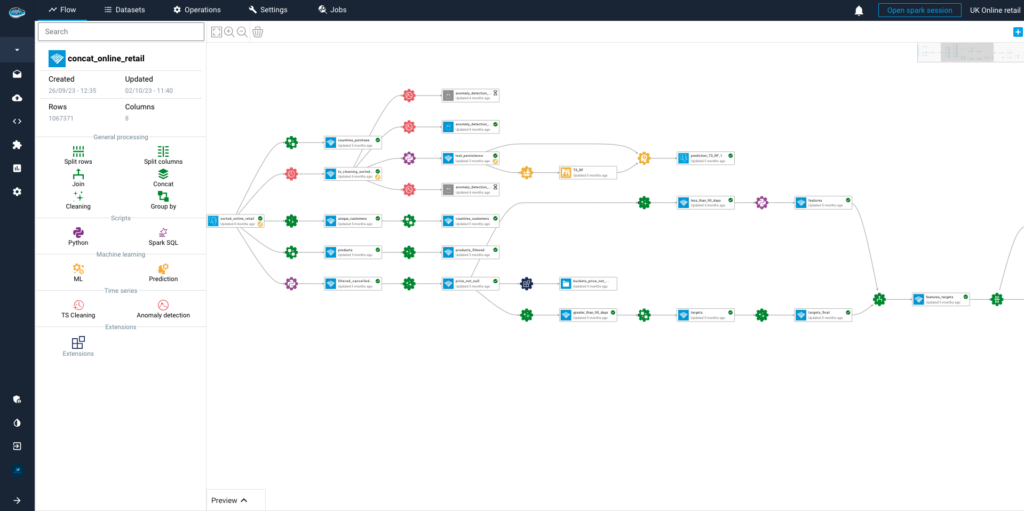
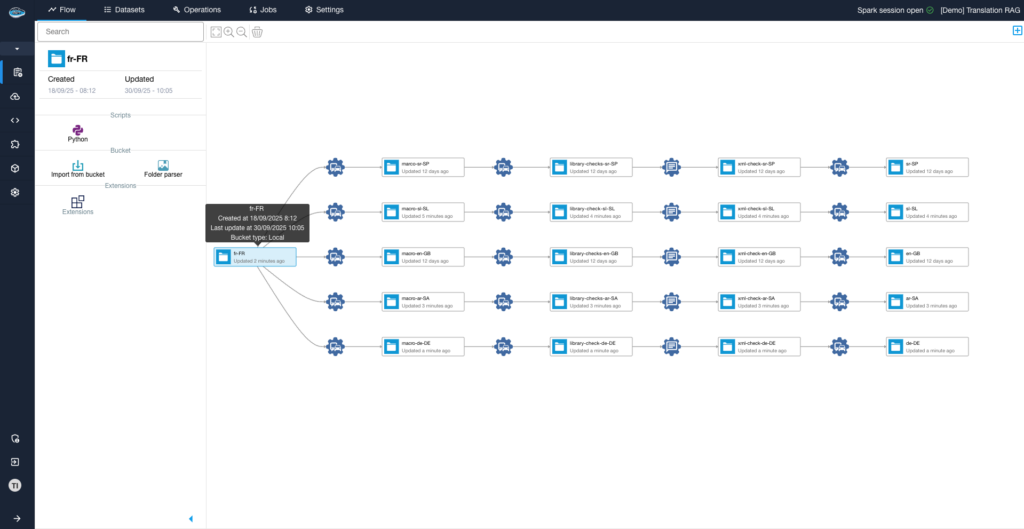
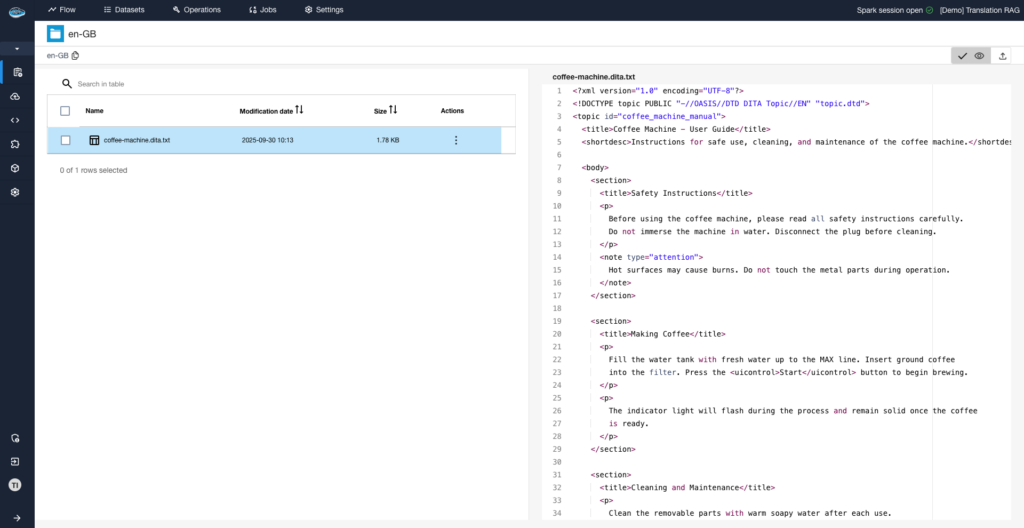
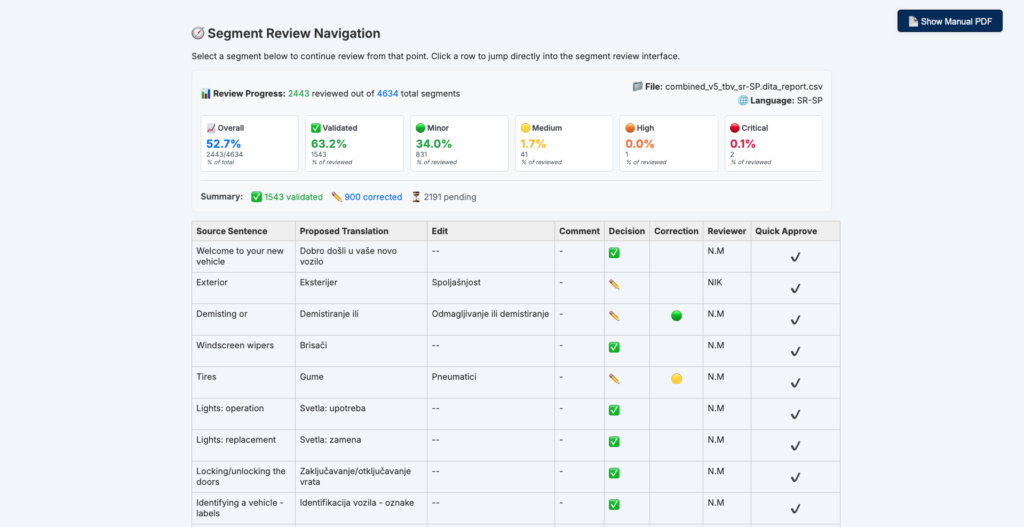
Why Should You Consolidate Your AI Tools for Faster Scaling?...
Read MoreLeverage papAI’s AI-powered translation capabilities today. Discover how your teams can accelerate global documentation workflows while maintaining absolute precision. Book a demo now and experience the next generation of AI-driven technical translation for the medical and life sciences industries.