Why Should You Consolidate Your AI Tools for Faster Scaling?...
Read MoreIn this article, we’ll explore how geospatial analytics is reshaping the way decisions are made, and why it’s quickly becoming a must-have in the modern data toolkit.
Table of Contents
ToggleMaking the right judgments in the fast-paced, data-driven world of today requires more than simply having more information; it also requires having the appropriate context. Geospatial analytics can help with that.
Organisations can detect trends, dangers, and opportunities that might otherwise go unnoticed by superimposing location data on top of conventional KPIs. Location intelligence is revolutionising a variety of industries, including supply chain optimisation, urban growth management, and natural disaster response.
Businesses leveraging geospatial data have seen an improvement in site selection accuracy by up to 65%. (Gartner’s Location Intelligence Report 2024, cited by Mindforce Research).
Find out how papAI can improve the deployment of AI projects in Sales Teams.

In this article, we’ll explore how geospatial analytics is reshaping the way decisions are made, and why it’s quickly becoming a must-have in the modern data toolkit.
Understanding the “where” of data is fundamental to geospatial analytics. It is the science and art of gathering, storing, modifying, and evaluating data with a geographic component. Consider it more as revealing hidden patterns, correlations, and trends within data due to its location than as merely examining maps.
Plotting locations on a globe is only one aspect of this; another is stacking other information, such as infrastructure, weather patterns, population demographics, and even social media check-ins, to uncover insights that would be hidden in a conventional spreadsheet. In the end, it enables us to respond to intricate enquiries concerning the reasons behind events and the spatial interactions of many components.
In essence, it helps us visualize and make sense of our complex world by providing a spatial context for decision-making, moving beyond simple data points to paint a comprehensive picture of interconnected events and opportunities across a landscape.
Spatial data, the “where” behind everything, is the foundation of geospatial analytics. This comprises the coordinates, forms, and borders that delineate tangible areas, such as a city’s layout or a delivery truck’s path. It’s what enables us to comprehend and map the physical environment digitally.
Attribute data informs us what, whereas spatial data tells us where. It’s the extra details that are connected to places, such the number of people living in an area, the speed limit on a road, or the kind of crop that is farmed there. It provides context for a location when paired with spatial data.
Geospatial analytics is made feasible by GIS technology. It is software that assists users in gathering, organising, analysing, and displaying both geographical and attribute data. From tracking disease outbreaks to mapping flood zones, GIS allows you to accomplish it all from a single platform.
These analytical techniques are applied to location data in order to glean insights. Examples include interpolation (predicting values between data points), cluster recognition (identifying patterns), and buffer analysis (calculating distance from a location). It’s how geographic data is transformed into knowledge that can be put to use.
Street addresses are transformed into geographic coordinates using geocoding. The opposite is true with reverse geocoding. These procedures assist in making traditional data, such as customer records, location-aware and map-ready by connecting them to actual locations.
Dashboards and interactive maps make data come to life. They facilitate faster trend recognition and better decision-making for non-experts. Visualisations, such as a heatmap of sales or a wildfire risk map, enable everyone to access geospatial data.
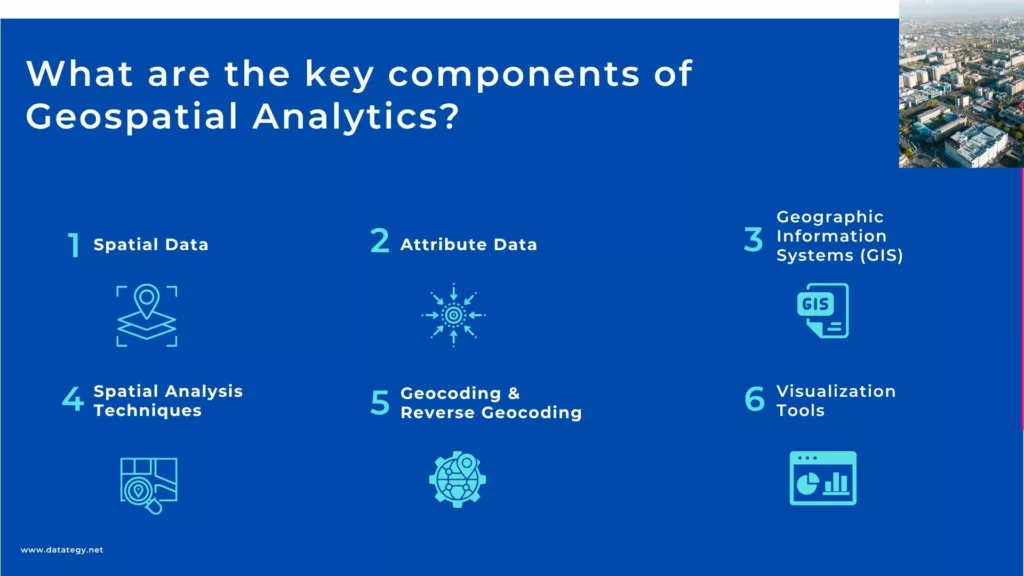
Key components of Geospatial Analytics
For maximizing resource utilisation and raising overall operational efficiency, geospatial analytics offers a potent perspective. It entails figuring out the quickest, most effective routes for logistics and transportation, cutting down on fuel usage, delivery delays, and overall operating expenses.
In order to minimise disturbance and maximise coverage, geospatial technologies can identify areas that require maintenance or where a new service line should be put. This is similar to how a utility company manages a massive network of infrastructure. By assisting farmers in applying fertiliser and water precisely where needed, it helps them save resources and increase harvests.
Companies can save a lot of money by allocating their resources, whether they be vehicles, workers, or materials, as efficiently as possible by knowing how assets and demands are distributed spatially.
Fundamentally, geospatial analytics converts intricate statistics into visually appealing formats that are simple to comprehend, such as interactive dashboards and maps. Seeing patterns and relationships that are hidden in raw data is more important than simply taking beautiful photographs.
Consider attempting to use spreadsheets of competitor locations, traffic statistics, and demographics to determine the ideal site for a new store. It’s almost impossible.
The best locations, however, become immediately apparent when you superimpose all of that data on a map. Businesses, governments, and organisations may make better, data-driven decisions much more quickly thanks to this visual depiction, which also lowers uncertainty and raises the possibility of successful results in a variety of operations, from disaster response to urban planning.
Sales and marketing are revolutionised when you know where your clients are and why they are there. Businesses can find optimal client demographics in particular regions by using geospatial analytics to segment markets based on geographic variables.
You can analyze purchasing patterns by location, understand foot traffic around potential store sites, or even track competitor locations to identify underserved markets. Highly targeted marketing campaigns are made possible by this profound spatial awareness, guaranteeing that promotional activities reach the appropriate individuals in the right places at the right time.
The outcome? Moving from generic outreach to highly personalised, location-aware methods will result in more successful campaigns, higher conversion rates, and ultimately a stronger return on marketing expenditure.
A forward-looking viewpoint provided by geospatial analytics is crucial for strategic planning and spotting new business prospects. Finding the ideal location for development in real estate involves examining zoning laws, accessibility to facilities, population growth patterns, and environmental aspects.
Based on demand trends and the presence of competitors, it assists companies seeking to grow in determining the best markets for new goods or services. It can be used by governments to plan their cities and choose the ideal sites for new hospitals, schools, or public transportation systems to accommodate expanding populations.
Geospatial analytics gives businesses a thorough, spatially aware picture of the environment, enabling them to make strategic, well-thought-out investments that promote long-term growth and competitive advantage.
To detect and reduce dangers before they become significant issues, geographic data visualisation and analysis skills are essential. By mapping regions vulnerable to natural catastrophes like floods or wildfires, geospatial technologies in environmental management can improve planning for evacuation and preparedness.
It aids in the strategic deployment of resources by law enforcement and the identification of crime hotspots for public safety. It can identify ageing bridges or pipelines that are highly likely to fail in infrastructure management, enabling preventative maintenance.
Organisations may improve safety procedures, create more effective risk management plans, and react to crises more skilfully by knowing the spatial distribution of possible risks and vulnerabilities. This helps to safeguard both human lives and property.

Geospatial analytics is indispensable for unlocking insights when the ‘where’ is as crucial as the ‘what’. It transforms abstract data into actionable intelligence, revealing patterns and relationships that would remain hidden in any other dimension.”
Jean-Marc Briquet
Global Sales Director-Datategy
The first thing you must do before utilising technology is to explicitly state your needs and the particular issues you hope to resolve with geospatial analytics. Don’t utilise it merely because it’s trendy. Identify specific business difficulties that location intelligence could help with by getting together with important stakeholders from various departments, such as sales, marketing, operations, logistics, urban planning, etc.
Do you wish to save fuel expenses by optimising delivery routes? Identify the best site for a brand-new retail establishment? Can you forecast client attrition in specific neighbourhoods? Track the performance of assets in the field? You can prove the ROI and gain internal support by establishing precise use cases and quantifiable, well-defined goals.
The quality of the data that geospatial analytics uses determines how good it is. After establishing your objectives, you must perform a comprehensive inventory of your current data.
Are you in possession of asset coordinates, client addresses, sales transaction locations, or operational site details? Is this data formatted consistently, accurately, and cleanly? Organisations frequently have important location data scattered across many systems, which may require extensive cleaning, standardisation, or “geocoding” (the process of translating addresses into exact latitude/longitude coordinates) before it can be put to use.
Think of other data sources that could enhance your study in addition to your internal data, such as rival locations, weather data, traffic patterns, demographic data, or public transportation routes. Additionally, you must evaluate your existing IT setup.
From open-source alternatives to complex business solutions, the market for geospatial analytics tools is broad and diverse. Your decision should be in line with your internal technological competence, budget, data types, and established business goals.
The use cases and business objectives you carefully outlined in the first phase must be directly reflected in your technology stack. You may require alternative technologies for complex predictive modelling of supply chain disruptions or real-time asset tracking over a large geographic area if your main objective is simple data visualisation on a map for executive presentations.
Don’t spend too much on features you won’t use, but don’t spend too little that your tools become a hindrance to future expansion. Think about the kinds and amounts of data you will be handling.
People from your business divisions who are able to interpret the analytical results in a meaningful context and who are aware of the unique difficulties and subtleties of your sector. To fill skill gaps, you may begin by acquiring new talent, educating current staff, or working with outside consultants.
Long-term success also depends on cultivating a data-driven culture within the company where staff members are motivated to investigate and use spatial findings. Your staff will stay current with new tools and practices in this quickly changing area if they participate in ongoing training and information exchange.
For the construction and administration of modern, effective cities, geospatial analytics is extremely essential. It is used by city planners to examine the distribution of green spaces, traffic patterns, infrastructural capacity (such as sewage systems, electrical grids, and water pipes), and population density.
Consider a city council deciding where to locate a hospital or a new public transportation line. In order to guarantee fair access, they will map out current routes using geospatial data, pinpoint regions with high demand or limited access, take environmental effects into account, and even take socioeconomic data into account. This aids in their data-driven decision-making on future development, resource allocation, and zoning.
Smart cities use geospatial knowledge for a variety of purposes, including optimising garbage collection routes according to bin full levels, in addition to large infrastructure.to putting in place sensor networks that keep an eye on noise pollution or air quality in particular communities, enabling real-time modifications and enhancements to urban living. It all comes down to comprehending the intricate interactions between the different parts of cities in space in order to make them more liveable, sustainable, and responsive to the demands of their residents.
Understanding “where” is crucial for firms to succeed, particularly in the retail industry. Companies can identify the ideal sites for new stores, eateries, or service facilities with the use of geospatial analytics.
Competitor locations, demographic information (age, income, and family size within a given radius), traffic numbers, visibility from main highways, accessibility to public transportation, and even customer loyalty programme data connected to addresses are all layered into this. While a calmer residential neighbourhood has the ideal demographic for their product, a merchant may find that an busy location is actually dominated by commuters who won’t stop.
In order to save fuel expenses and delivery times, it is also utilised for supply chain optimisation, warehouse placement planning, and delivery route planning. Additionally, by enabling companies to deliver promotions straight to prospective clients who live or work close to a certain store, it strengthens targeted marketing campaigns and improves return on marketing investment.
Understanding spatial relationships is crucial to protecting our world, and geospatial analytics excels in this regard. It is used by conservation groups and environmental authorities to measure rates of deforestation, follow changes in land use over time, and evaluate how climate change is affecting particular ecosystems.
For example, they can monitor the water quality in rivers and lakes, detect illicit logging, and track the spread of exotic species by combining satellite imagery and data from ground sensors. Additionally, it is essential for maintaining protected areas, tracking animal migration routes, identifying important ecosystems, and conserving species.
Geospatial tools are used instantly to map the degree of damage, identify impacted populations, and direct emergency response activities when a natural catastrophe occurs, such as a flood or wildfire. Geospatial analytics helps scientists and policymakers make well-informed decisions for conservation and sustainable resource management by giving them a clear, visual picture of environmental dynamics.
Food production is going to become more “spatial.” Precision agriculture, which is more sustainable and efficient than traditional farming, is being created by geospatial analytics. Farmers produce incredibly accurate maps of their land using sensors positioned in fields, drone data, and satellite photography.
Variations in soil health, nutrient levels, moisture content, and even crop health down to the individual plant level can all be seen on these maps. Instead of applying water, fertiliser, and pesticides evenly over the field, this enables farmers to distribute them exactly where they are needed. This lessens the impact on the environment in addition to saving money on inputs.
It aids in yield prediction, pest or disease susceptibility identification, and planting and harvesting schedule optimisation. Higher crop yields, less waste, and a more sustainable method of producing food that makes use of location intelligence to increase productivity and lessen environmental impact are the outcomes.
Although geospatial analytics presents amazing opportunities, it is not without its difficulties, and the first one is frequently data quality. The insights you obtain may be deceptive if the data that feeds your maps or models is out-of-date, inconsistent, or lacking in important details.
This is particularly true for location-based data, where even minor inaccuracies in timestamps or locations can disrupt an entire analysis. Clean, verified data from reliable sources must be prioritised by organisations, which frequently takes more time and work than anticipated.
Accessibility is still another significant obstacle. Even if there are strong tools available, not everyone can use them. Because many geospatial platforms are still sophisticated and designed for experts, teams without a background in GIS may find it challenging to fully utilise them.
Furthermore, smaller businesses or developing regions may be unable to fully adopt geospatial insights due to licensing fees, a lack of publicly available information, or geographical constraints. Although the movement towards open data and no-code technologies is beneficial, more has to be done.
In this white paper, we provide an overview of AI solutions on the market. We give you concrete guidelines to choose the solution that reinforces the collaboration between your teams.

From analysts to domain experts, papAI is an end-to-end AI and analytics platform that aims to make advanced data science available to all teams. papAI facilitates the intersection of your data and the actual world, whether you’re working with satellite imagery or business KPIs. Because it combines location intelligence with strong, intuitive AI technologies, it stands out in the field of geospatial analytics.
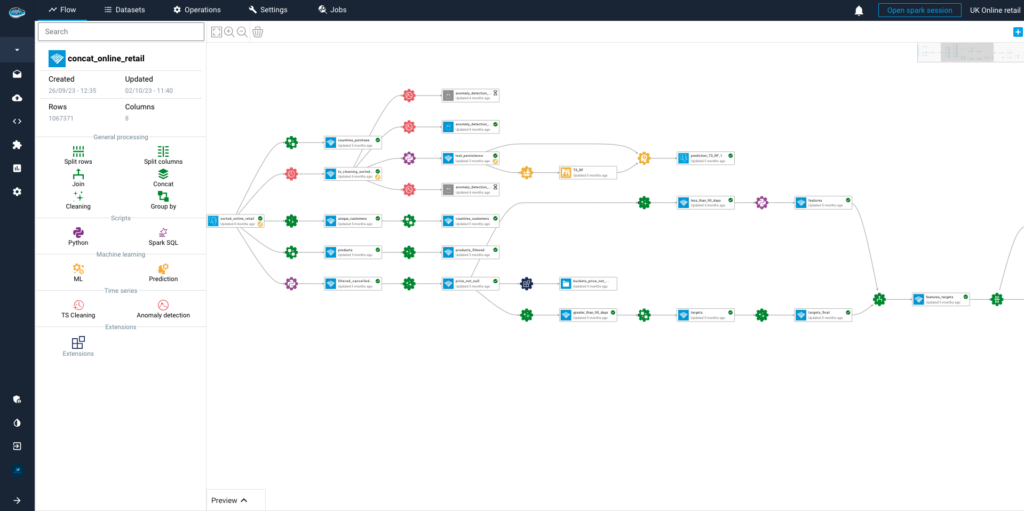
Measuring a brand’s influence and strategy requires an understanding of how it changes over time. Using geospatial information, we examine the brand’s retail expansion journey throughout the United States in this visualization, showing how its footprint increased consistently between 2013 and 2017.
Without writing a single line of code, teams can quickly visualise trends, create year-over-year geographical insights, and input location data with ease thanks to papAI. Organisations can track growth, optimise territorial planning, and clearly support data-driven decisions with the aid of this type of time-based geographic storytelling.
5 Years of Strategic Retail Growth on papAI
Here’s an in-depth look at the key features and advantages of this innovative solution:
With papAI, users can easily upload and manipulate geographic data in a variety of forms, including as coordinate-based datasets, shapefiles, GeoJSON, and raster pictures. Whether you’re mapping transportation routes, environmental zones, or retail locations, the platform takes care of the geolocation layer.
Additionally, it integrates seamlessly with external GIS systems or spatial databases, facilitating the integration of location information and business data. No complicated workflows or manual conversions are required; simply import your spatial data and begin exploring.
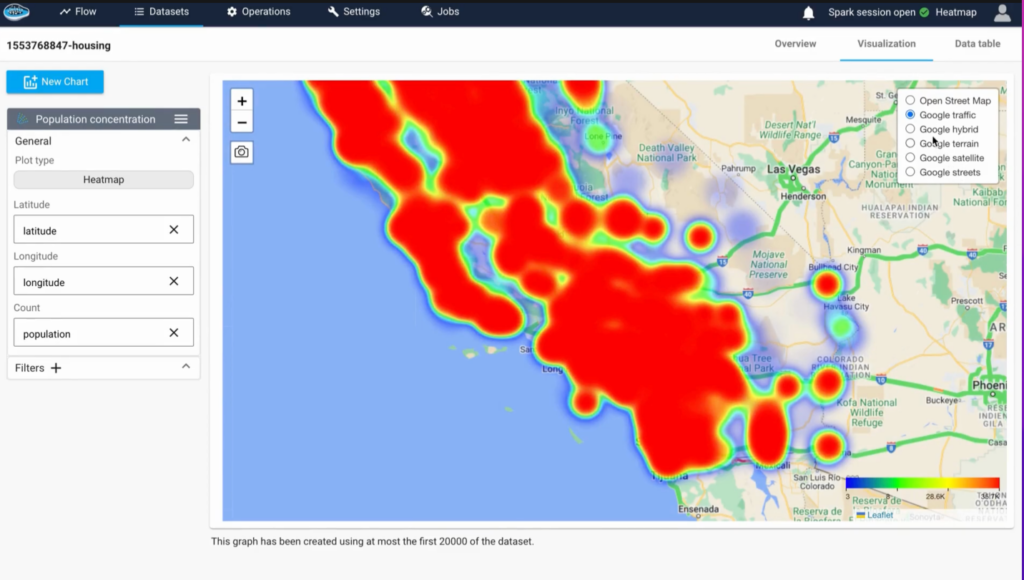
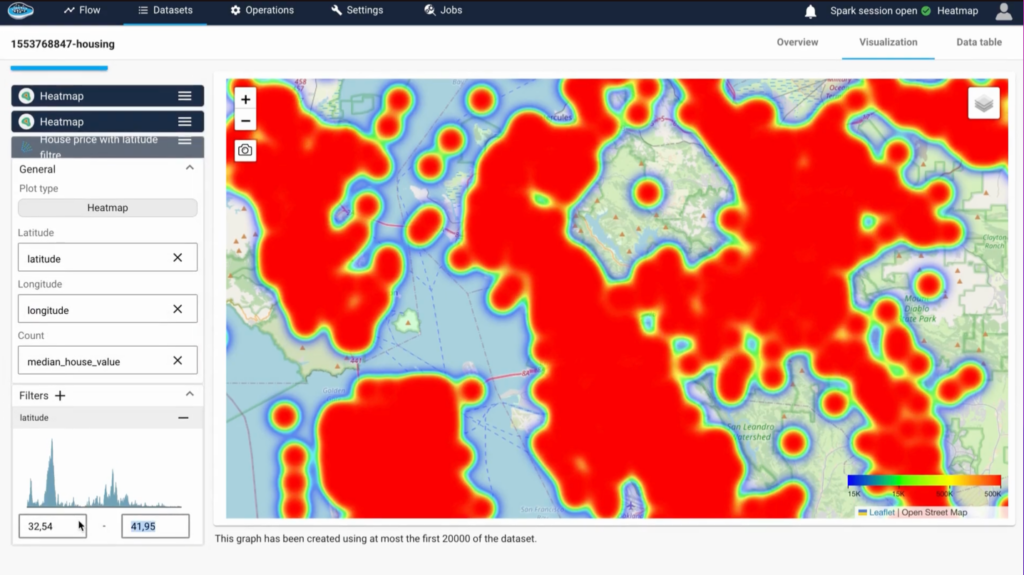
The capacity of papAI to transform complicated data into understandable, interactive graphics is one of its main advantages. Users may create real-time updating geospatial dashboards, heatmaps, and layered maps with a few clicks.
Finding trends, comparing locations, and sharing insights with decision-makers who might not be familiar with raw data are all made simple by these tools. PapAI enables you to see the narrative behind your spatial data, whether you’re tracking deliveries or keeping an eye on energy grids.
papAI extends the capabilities of AI beyond visualizations to geographical analysis. Models can be created to forecast future demand, emerging dangers, and changes in spatial patterns across time. For instance, cities can use it to model environmental effect scenarios, and shops can anticipate foot traffic by area. Teams may go from observation to prediction with the aid of the platform’s AI layer, which deepens conventional spatial analysis.
Geospatial analytics is becoming a need rather than a luxury in a world where every choice is linked to a location. Location-based insights provide a significant advantage whether you’re following retail expansion, building public infrastructure, or keeping an eye on environmental threats.
Using papAI makes it easy to realize this potential. To transform raw location data into understandable, workable plans, you don’t need to be a data scientist or a GIS specialist. Book your demo now.
In essence, it helps us visualize and make sense of our complex world by providing a spatial context for decision-making, moving beyond simple data points to paint a comprehensive picture of interconnected events and opportunities across a landscape.
Geospatial analytics adds a “where” to the “what” by looking at more than simply numbers. Patterns that would otherwise be overlooked are revealed by examining the location or spatial dimension of data. Geospatial analytics provides a strong layer of context that is frequently essential for decision-making, whether it is mapping supply chain hazards or detecting customer clusters.
Retailers choosing shop locations, governments overseeing infrastructure, and energy companies maximising grid coverage are just a few examples of the organisations that stand to gain from location-based decision-making. In industries where geography, mobility, and territory have a direct impact on strategy and performance, the insights obtained through geospatial analytics are particularly beneficial.
Data quality, as spatial data can be inconsistent or incomplete.
Access to specialized tools, since traditional GIS platforms can be complex.
Skills gap, where teams lack the training to interpret spatial insights.
papAI helps overcome these by offering a unified platform with user-friendly tools and built-in AI support.
Interested in discovering papAI?
Our AI expert team is at your disposal for any questions
Why Should You Consolidate Your AI Tools for Faster Scaling?...
Read MoreWhy is Deployment Speed the New 2026 AI Moat? The...
Read MoreWe Don’t Just Build AI, We Deliver Measurable Impact Join...
Read MoreAI’s Role in Translating Complex Defence Documentation The defence sector...
Read More

| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |